1. General
Valves of this series are used to close or open pipelines in pipeline system so as to maintain normal operation of the system.
2. Product Description
2.1Technique requirement
2.1.1 Design and manufacture: API600、API603、ASME B16.34、BS1414
2.1.2 Connection end dimension:ASME B16.5、ASME B16.47、ASME B16.25
2.1.3 Face to face or end to end:ASME B16.10
2.1.4 Inspection and test:API 598、API600
2.1.5 Nominal sizes:MPS2″~48″,Nominal class ratings:Class150~2500
2.2 Valves of this series are manual (actuated through handwheel or gear box) gate valves with flange ends and butt welding end .The valve stem moves vertically. When turn the handwheel clockwise, the gate falls down to close the pipeline; when turn the handwheel counterclockwise, the gate rises up to open pipeline.
2.3 The structural see Fig.1, 2and3.
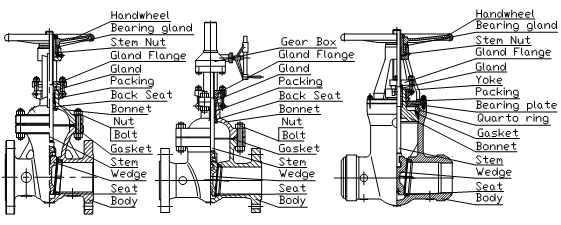
2.4 Names and materials of main parts are listed in Table 1.
| Part Name | Material |
| Body and bonnet |
ASTM A216 WCB、ASTM A352 LCB、ASTM A217 WC6、 ASTM A217 WC9、ASTM A351 CF3、ASTM A351 CF3M ASTM A351 CF8、ASTM A351 CF8M、ASTM A351 CN7M ASTM A494 CW-2M、Monel |
| gate |
ASTM A216 WCB、ASTM A352 LCB、ASTM A217 WC6、 ASTM A217 WC9、ASTM A351 CF3、ASTM A351 CF3M ASTM A351 CF8、ASTM A351 CF8M、ASTM A351 CN7M ASTM A494 CW-2M、Monel |
| seat |
ASTM A105、ASTM A350 LF2、F11、F22、 ASTM A182 F304(304L)、ASTM A182 F316(316L) ASTM B462、Has.C-4、Monel |
| stem |
ASTM A182 F6a、ASTM A182 F304(304L) 、ASTM A182 F316(316L)、ASTM B462、Has.C-4、Monel |
| Packing | Braided graphite and flexible graphite、PTFE |
| Stud/nut |
ASTM A193 B7/A194 2H、ASTM L320 L7/A194 4、 ASTM A193 B16/A194 4、ASTM A193 B8/A194 8、 ASTM A193 B8M/A194 8M |
| Gasket |
304(316)+Graph、304(316)、Has.C-4、 Monel、B462 |
| Seat ring/Disc/surfaces | 13Cr、18Cr-8Ni、18Cr-8Ni-Mo、NiCu alloy、25Cr-20Ni、STL |
3. Storage, maintenance, Installation and operation
3.1 Storage and maintenance
3.1.1 The valves should be stored in dry and well ventilated room. The passage ends should be plugged with covers.
3.1.2 The valves under long-time storage should be examined and cleaned regularly, especially the cleaning of seating face to prevent damage, and the finished surfaces should be coated with rust inhibiting oil.
3.1.3 If storage period exceeds 18 months, the valves should be tested and records should be made.
3.1.4 Installed valves should be examined and repaired regularly. The main maintenance points include the following:
1)Sealing face
2)Valve stem and valve stem nut.
3)Packing.
4)Fouling on internal surface of valve body and valve bonnet
3.2 Installation
Before installation, make sure valve identification (such as model, DN, 3.2.1PN and material) are marked according to requirements of pipeline system.
3.2.2 Before installation, carefully check valve passage and sealing face. If there is any dirt, clean it thoroughly.
3.2.3 Before installation, make sure all bolts are fastened tightly.
3.2.4 Before installation, make sure packing is compressed tightly. However, the motion of valve stem should not be disturbed.
3.2.5 The installation place of the valve should facilitate inspection and operation. The preferable position should be that the pipeline is horizontal, handwheel is above, and valve stem is vertical.
3.2.6 For normally closed valve, it is not suitable to install it in the place where working pressure is very big to avoid damage of valve stem.
3.2.7 Socket welded valves shall at least meet the following requirements when they are welded for installation in pipeline system on site:
1) Welding should be carried out by the welder who possesses welder’s qualification certificate approved by the State Boiler and Pressure Vessel Authority; or the welder who has obtained welder’s qualification certificate specified in ASME Vol.Ⅸ.
2) Welding process parameters must be selected as specified in the quality assurance manual of welding material.
3) The chemical composition, mechanical performance and corrosion resistance of the filler metal of welding seam should be compatible with base metal.
3.2.8 The valve is normally installed, big stress due to supports, accessories and pipes should be avoided.
3.2.9 After installation, during pressure testing of pipeline system, the valve must be fully opened.
3.2.10 Bearing point: if the pipeline has sufficient strength to bear valve weight and operation torque, then no bearing point is required, otherwise valve should have bearing point.
3.2.11 Lifting: don’t use handwheel to hoist and lift valve.
3.3 Operation and use
3.3.1 During service period, valve gate must be fully opened or fully closed to avoid surface damage of seat ring and valve gate due to high-speed medium. It cannot be used to adjust flow capacity.
3.3.2 When open or close the valve, use handwheel instead of auxiliary lever or use other tool.
3.3.3 At working temperature, make sure instantaneous pressure be lower than 1.1times that working pressure of pressure-temperature ratings in ASME B16.34.
3.3.4 Safety relief equipment should be installed on the pipeline to prevent the working pressure of the valve at working temperature from exceeding the maximum allowable pressure.
3.3.5 Stroking and shocking the valve is prohibited during transport, installation and operation period.
3.3.6 Decomposition of unsteady fluid, for example, the decomposition of some fluids can cause volume expansion and lead to working pressure rise, thus damaging the valve and causing permeation, therefore, use appropriate measuring instruments to eliminate or limit factors that may cause decomposition of fluid.
3.3.7 If the fluid is a condensate, this will affect valve performance, use appropriate measuring instruments to reduce temperature of the fluid (for example, to guarantee appropriate temperature of the fluid) or replace it with other type of valve.
3.3.8 For self-inflammable fluid, use appropriate measuring instruments to guarantee ambient and working pressure do not exceed its auto-ignition point (especially notice sunshine or external fire).
3.3.9 In case of dangerous fluid, such as explosive, inflammable. Toxic, oxidation products, it is prohibited to replace packing under pressure (although the valve has such a function).
3.3.10 Make sure the fluid is not dirty, which affects valve performance, does not contain hard solids, otherwise appropriate measuring instruments should be used to remove the dirt and hard solids, or replace it with other type of valve.
3.3.11 Allowable working temperature:
|
Material |
temperature |
Material |
temperature |
|
ASTM A216 WCB |
-29~425℃ |
ASTM A217 WC6 |
-29~538℃ |
|
ASTM A352 LCB |
-46~343℃ |
ASTM A217 WC9 |
--29~570℃ |
|
ASTM A351 CF3(CF3M) |
-196~454℃ |
ASTM A494 CW-2M |
-29~450℃ |
|
ASTM A351 CF8(CF8M) |
-196~454℃ |
Monel |
-29~425℃ |
|
ASTM A351 CN7M |
-29~450℃ |
|
- |
3.3.12 Make sure the material of valve body is suitable for use in corrosion resistant and rust prevention fluid environment.
3.3.13 During service period, examine sealing performance as per the table below:
|
Inspection point |
Leak |
|
Connection between valve body and bonnet |
Zero |
|
Packing seal |
Zero |
|
Valve seat |
As per technical specification |
3.3.14 Regularly check for the wear of sealing face. Packing aging and damage. Make repair or replacement in time if evidence is found.
3.3.15 After repair, re-assemble and adjust the valve, the test tightness performance and make record.
3.3.16 Examination and repair internal is two years.
4. Possible problems, causes and remedial measures
|
Problem description |
Possible cause |
Remedial measures |
|
Leak at packing |
Insufficiently compressed packing |
Re-tighten packing nut |
|
Inadequate quantity of packing |
Add more packing |
|
|
Damaged packing due to long-time service or improper protection |
Replace packing |
|
|
Leak on valve seating face |
Dirty seating face |
Remove dirt |
|
Worn seating face |
Repair it or replace seat ring or valve gate |
|
|
Damaged seating face due to hard solids |
Remove hard solids in the fluid, repair or replace seat ring or valve gate, or replace with other type of valve |
|
|
Leak at connection between valve body and valve bonnet |
Bolts are not properly fastened |
Uniformly fasten bolts |
|
Damaged seating surface of valve body and valve bonnet flange |
Repair it |
|
|
Damaged or broken gasket |
Replace gasket |
|
|
Difficult rotation of handwheel or valve gate cannot be opened or closed |
Too tightly fastened packing |
Appropriately loosen packing nut |
|
Deformation or bending of sealing gland |
Adjust sealing gland |
|
|
Damaged valve stem nut |
Correct thread and remove the dirt |
|
|
Worn or broken valve stem nut thread |
Replace valve stem nut |
|
|
Bent valve stem |
Replace valve stem |
|
|
Dirty guide surface of valve gate or valve body |
Remove dirt on guide surface |
Note: Service person should have relevant knowledge and experience with valves.
5. Warranty
After the valve is put into use, the warranty period of valve is 12 months, but does not exceed 24 months after delivery date. During warranty period, the manufacturer will provide repair service or spare parts free of charge for the damage due to material, workmanship or damage provided that operation is correct.
Post time: May-19-2022

